1 | updateStateByKey: |
1 | [double_happy@hadoop101 ~]$ nc -lk 9999 |
1 | object StreamingWCApp01 { |
The updateStateByKey operation allows you to maintain arbitrary state while continuously updating it with new information. To use this, you will have to do two steps.
1.Define the state - The state can be an arbitrary data type.
2.Define the state update function - Specify with a function how to update the state
using the previous state and the new values from an input stream.
In every batch, Spark will apply the state update function for all existing keys, regardless of whether they have new data in a batch or not. If the update function returns None then the key-value pair will be eliminated.
Let’s illustrate this with an example. Say you want to maintain a running count of each word seen in a text data stream. Here, the running count is the state and it is an integer. We define the update function as:
1 | updateStateByKey operation : |
案例:
1 | 1. |
1 | object StreamingWCApp01 { |
修改代码
1 | [double_happy@hadoop101 ~]$ nc -lk 9999 |
1 | object StreamingWCApp01 { |
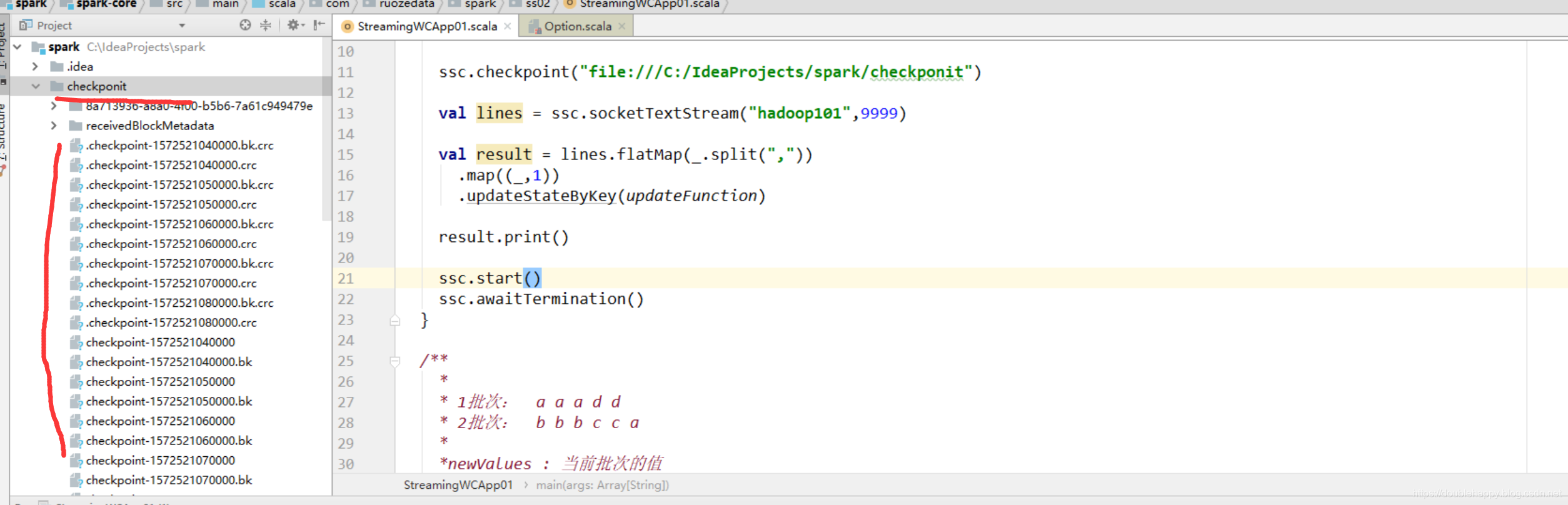
1 | ok 现在我把程序关掉 重启以后 是多少呢? |
1 | 最好直接看官网:我只是截取我认为重要的 |
1 | object StreamingWCApp02 { |
1 | [double_happy@hadoop101 ~]$ nc -lk 9999 |
1 | 结果: |
1 | Stream + Kafka == CP |
把数据写出去: ****
1 | foreachRDD: |
把数据写到MySQL
1 | MySQL底层引擎有几种?各自什么区别? |
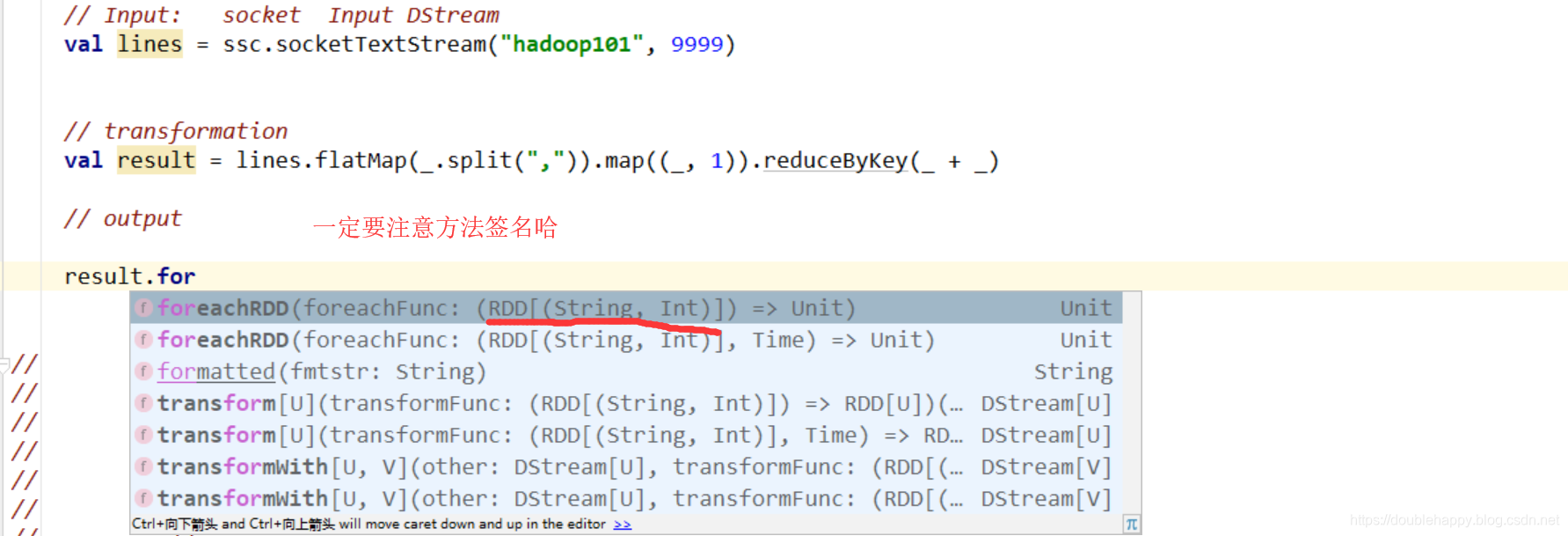
咱们一步一步来 由劣到优
1 | object StreamingWCApp03 { |
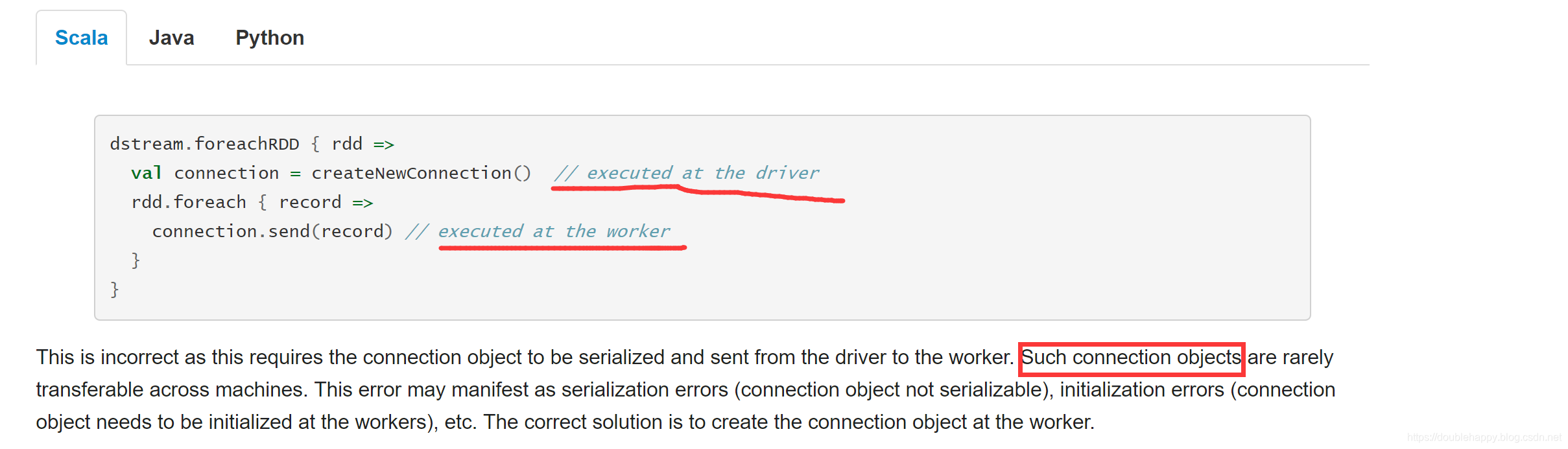
华丽的分割线————————————————————————————————————
1 | 上面的错误明白之后 那么什么叫做闭包? |
1 | 闭包:在函数内部 引用了一个外部的变量 |
修改:
1 | result.foreachRDD( rdd =>{ |
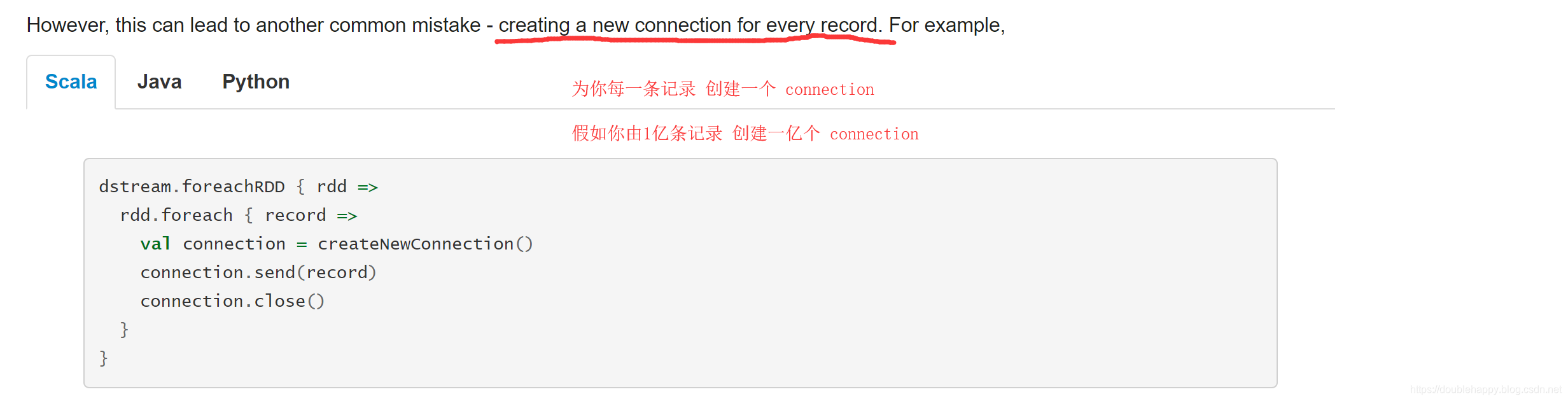
优化
1 | object StreamingWCApp03 { |
1 | 正确的写法会写了 但是 |
还有一种写法 建议使用它
scalikejdbc 自带Connection Pool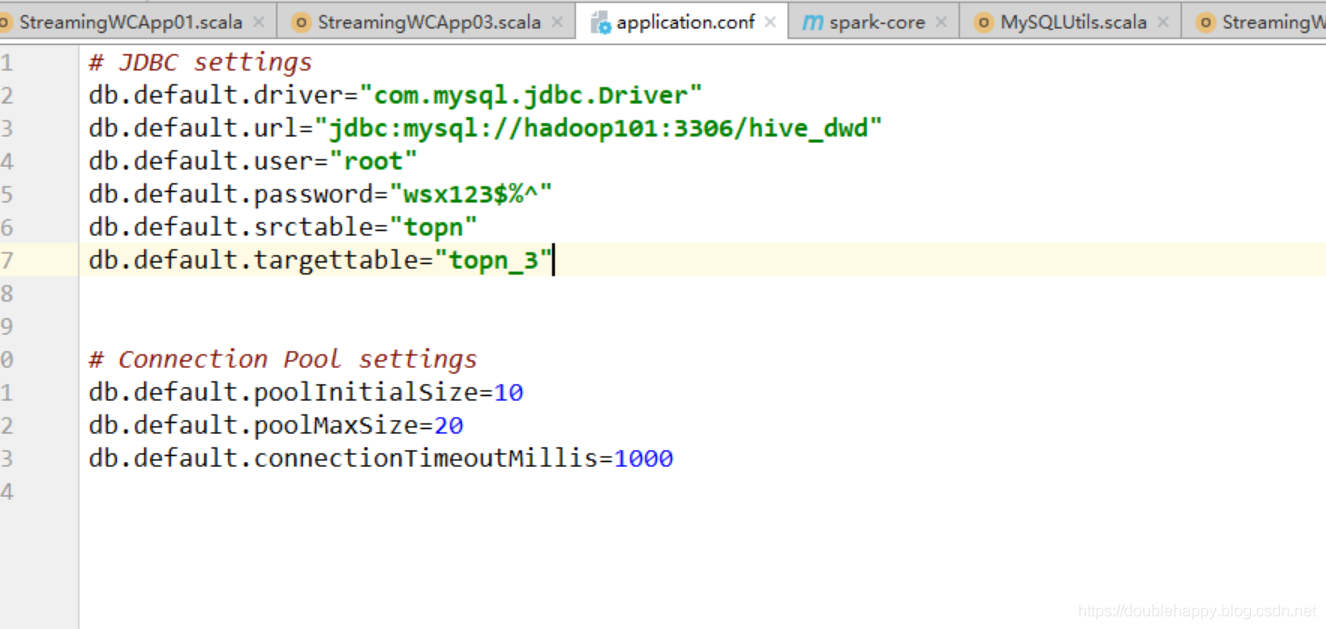
1 | object StreamingWCApp03 { |
1 | 之前 我们用state 进行累计的 |
1 | object StreamingWCApp03 { |
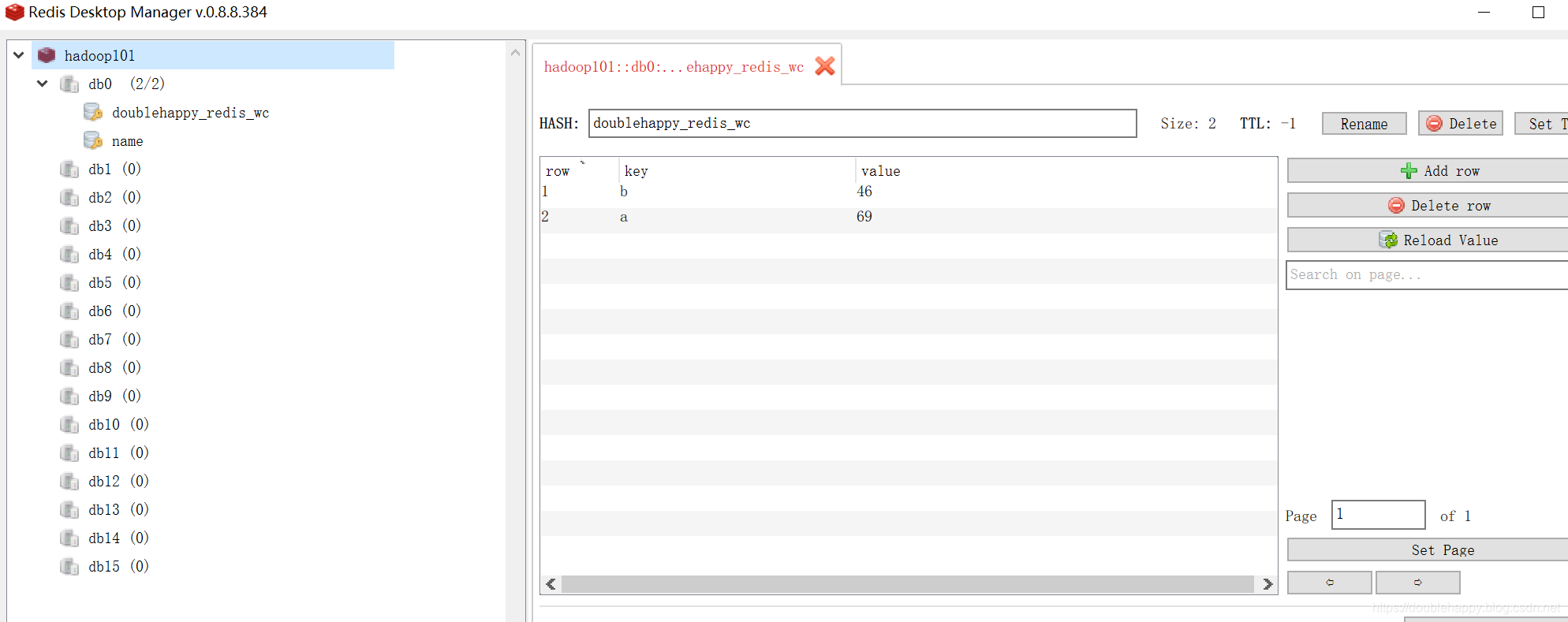
1 | 再放一些数据 |
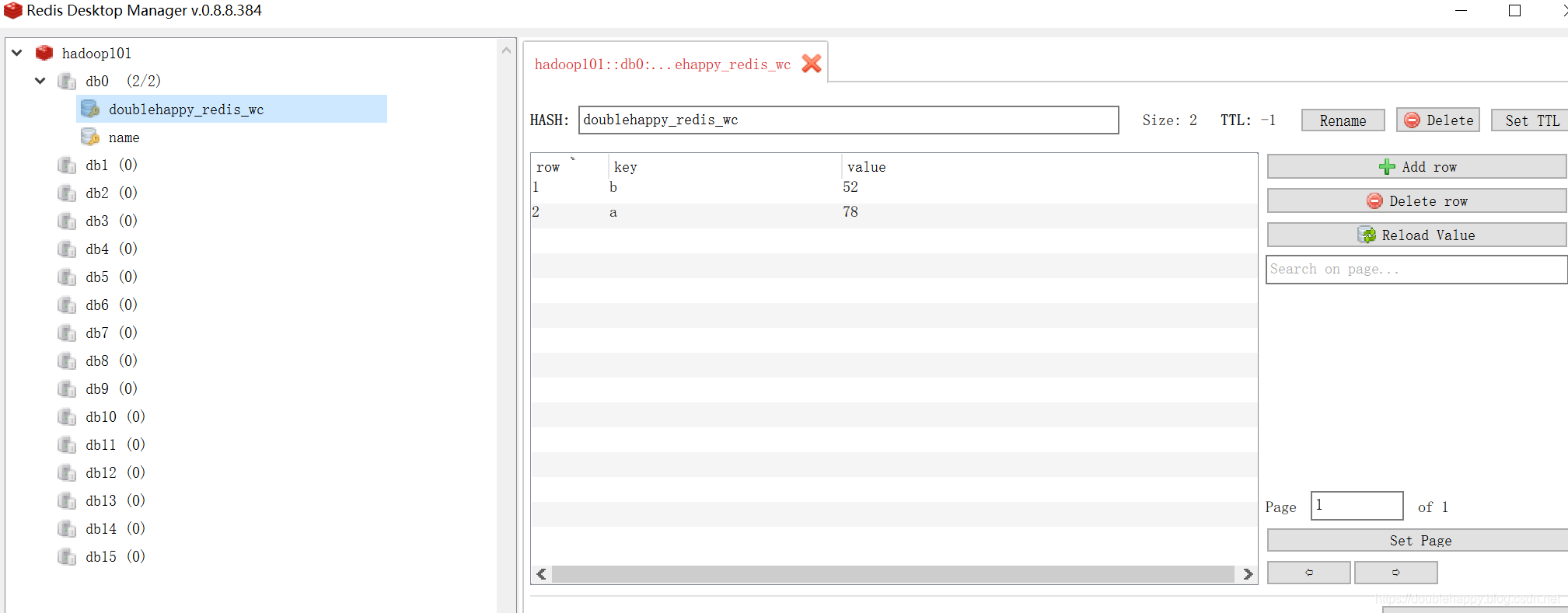
说明结果ok的哈
transform
transform
1 | transform(func) ; |
例子
黑名单
目的:
只要由黑名单里的东西 把黑名单的数据全部过滤掉
1 | 先用core的方式; |
1 | ssc:很重要 |