1 | Fault Tolerance: |
1 | 流处理 |
1 | 1. Spark Streaming is an extension of the core Spark API |
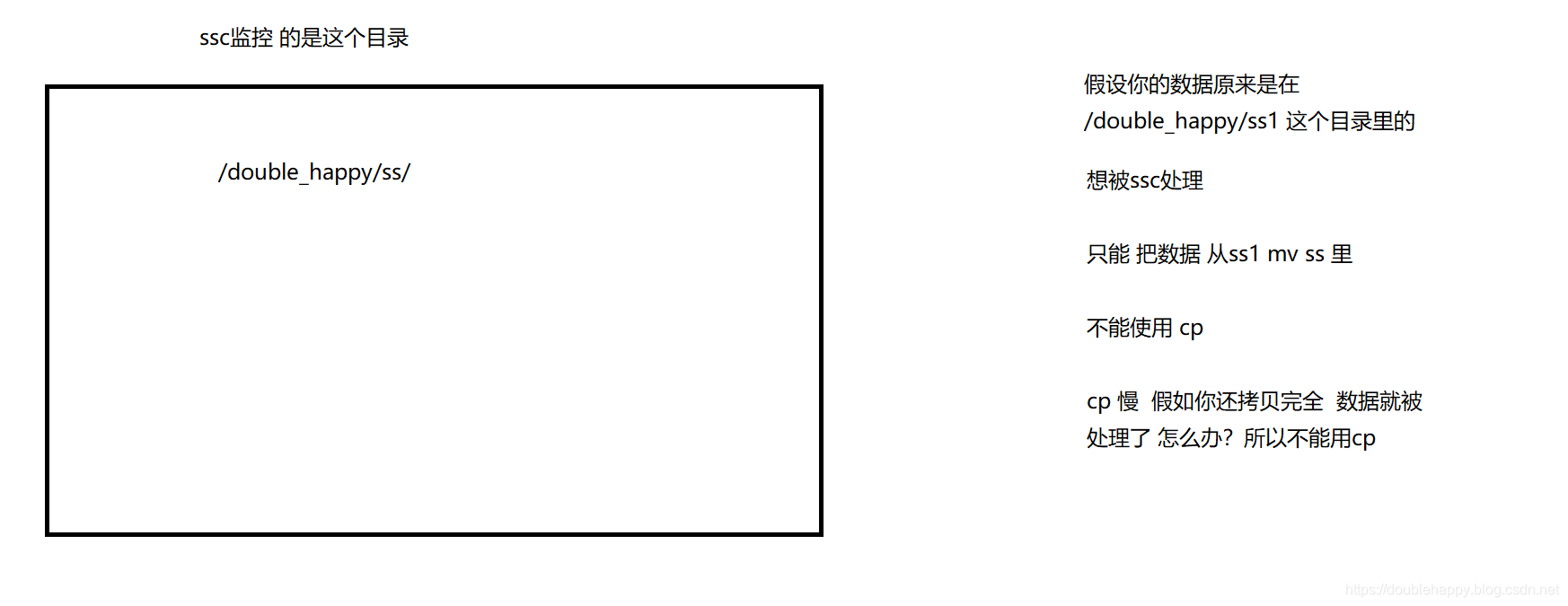
1 | ss: |
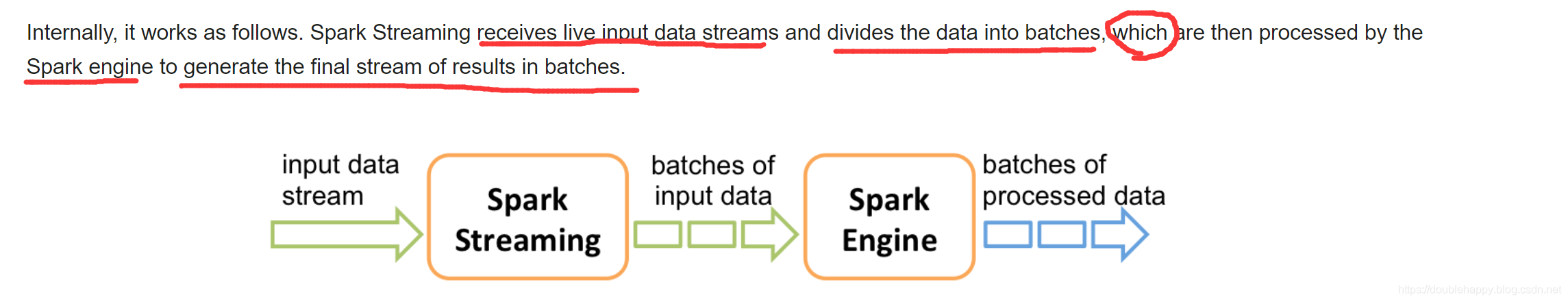
1 | Spark Streaming 的编程模型: |
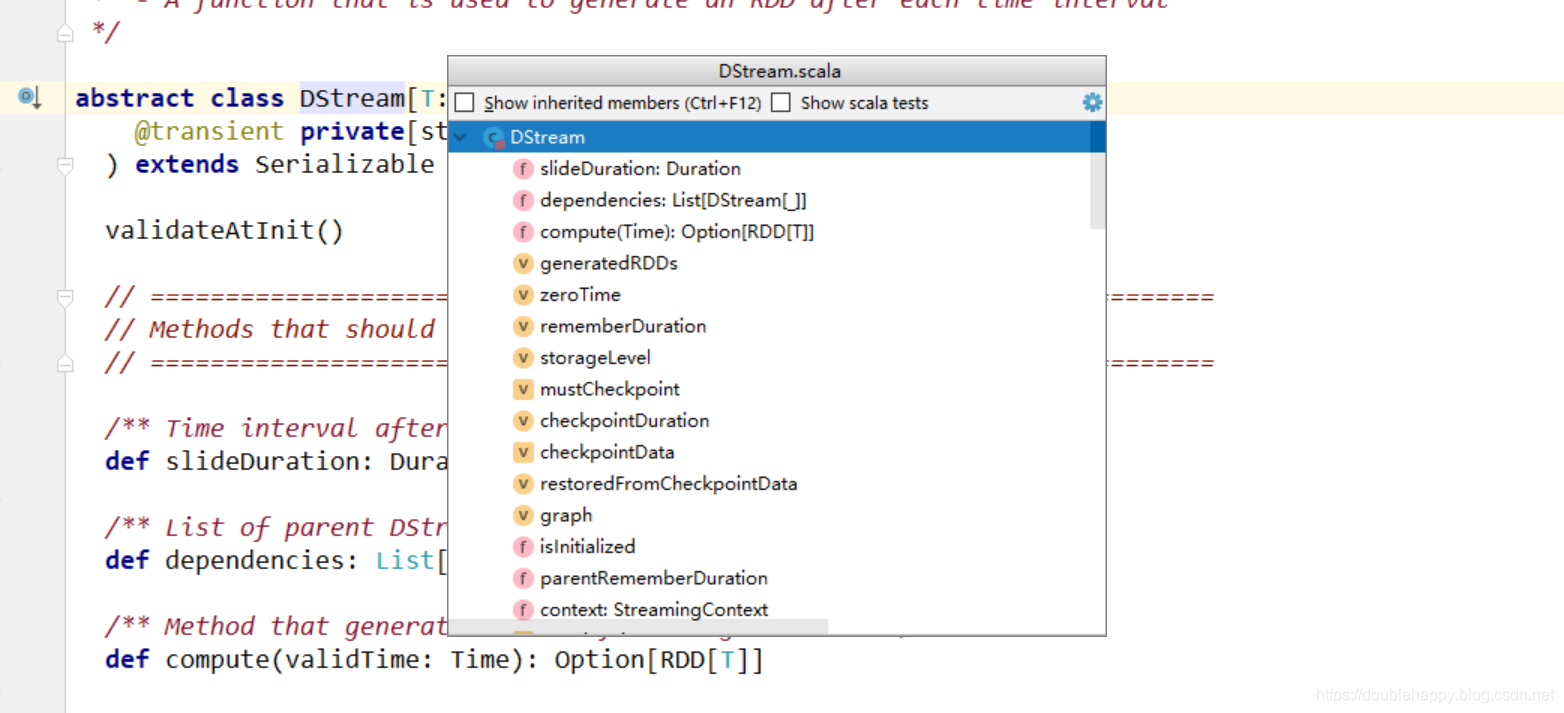
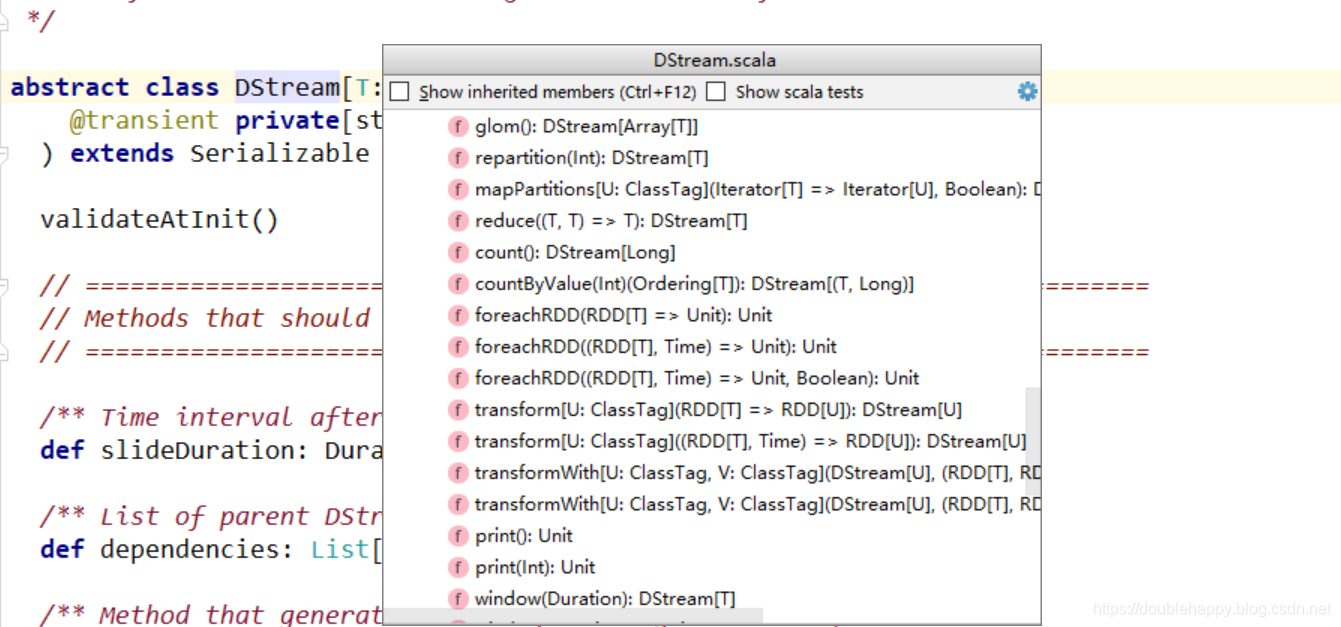
1 | 所以RDD算子一点要熟练掌握 |
案列代码准备
1 |
|
1 | 封装一个工具类: |
1 | object AppName { |
案例
socket: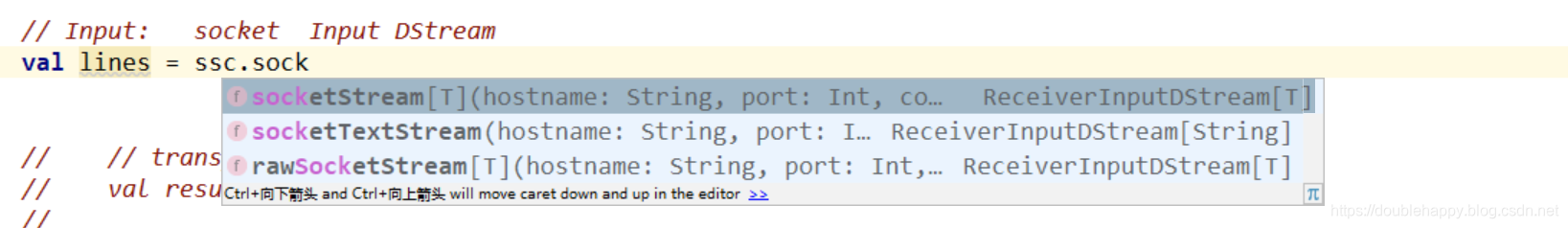
1 | 有三个 :用哪个呢?有什么区别呢?看下面 |
1 | 数据源:socket |
测试:
1 | [double_happy@hadoop101 ~]$ nc -lk 9999 |
1 | object StreamingWCApp01 { |
1 | [double_happy@hadoop101 ~]$ nc -lk 9999 |
1 | After a context is defined, you have to do the following. |
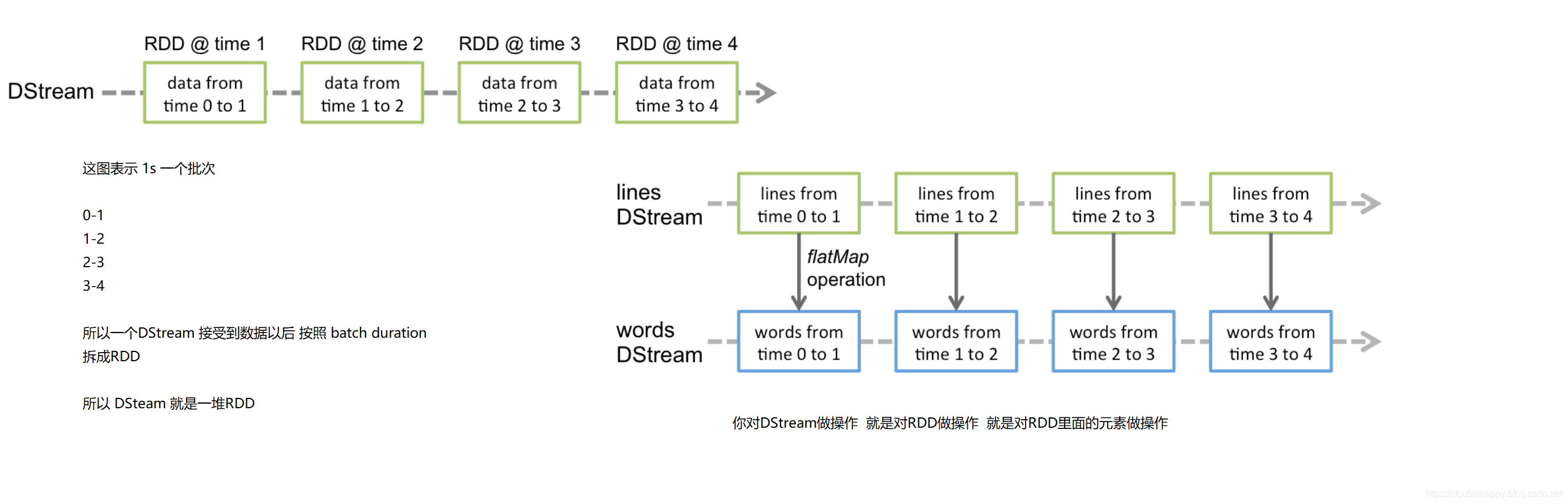
1 | 上面案例讲解: |
Input DStreams are DStreams representing the stream of input data received from streaming sources. In the quick example, lines was an input DStream as it represented the stream of data received from the netcat server. Every input DStream (except file stream, discussed later in this section) is associated with a Receiver (Scala doc, Java doc) object which receives the data from a source and stores it in Spark’s memory for processing.
1 | 1. lines was an input DStream |

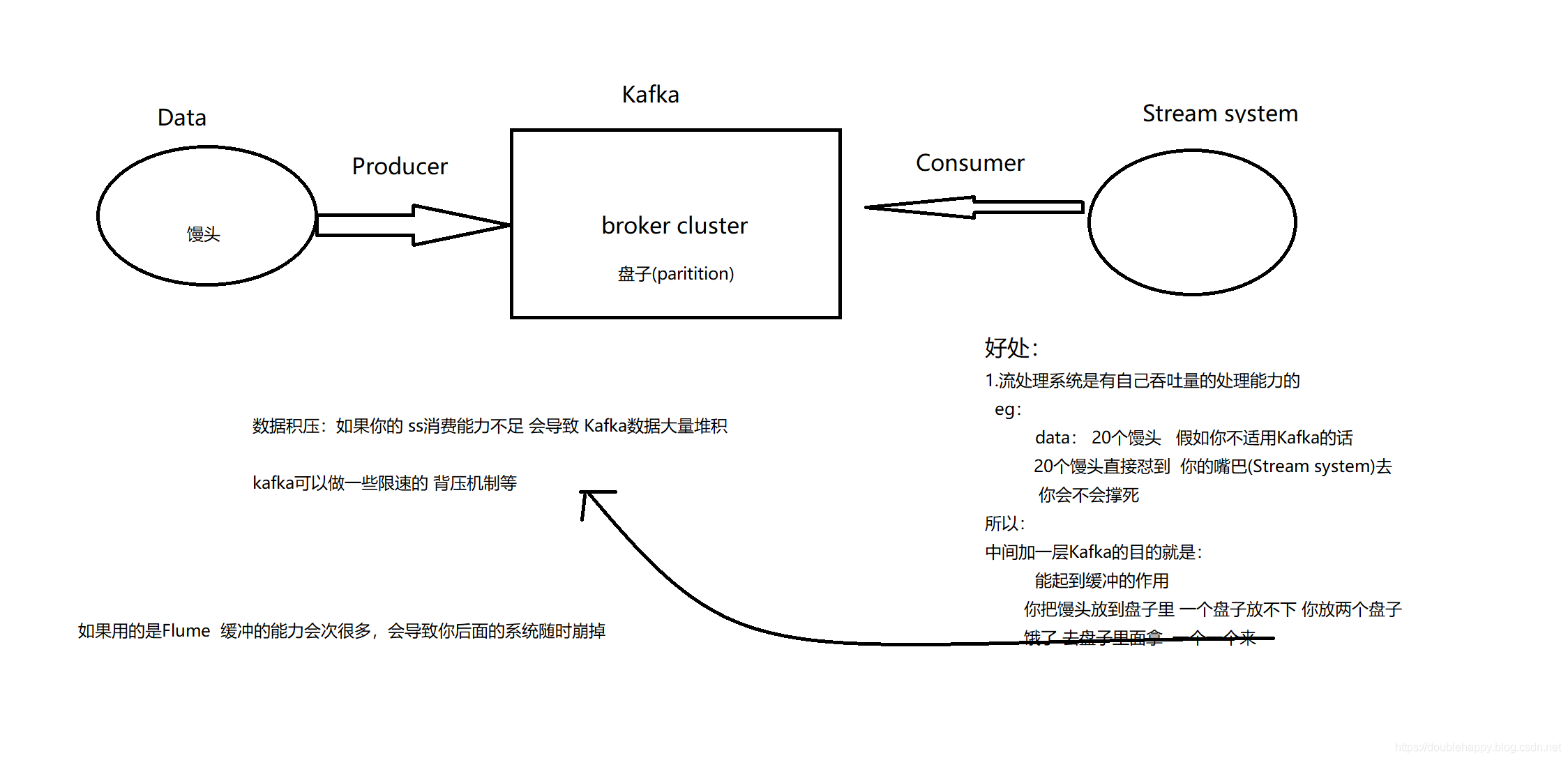
1 | where > n 因为 有些业务是需要多个流处理的 |
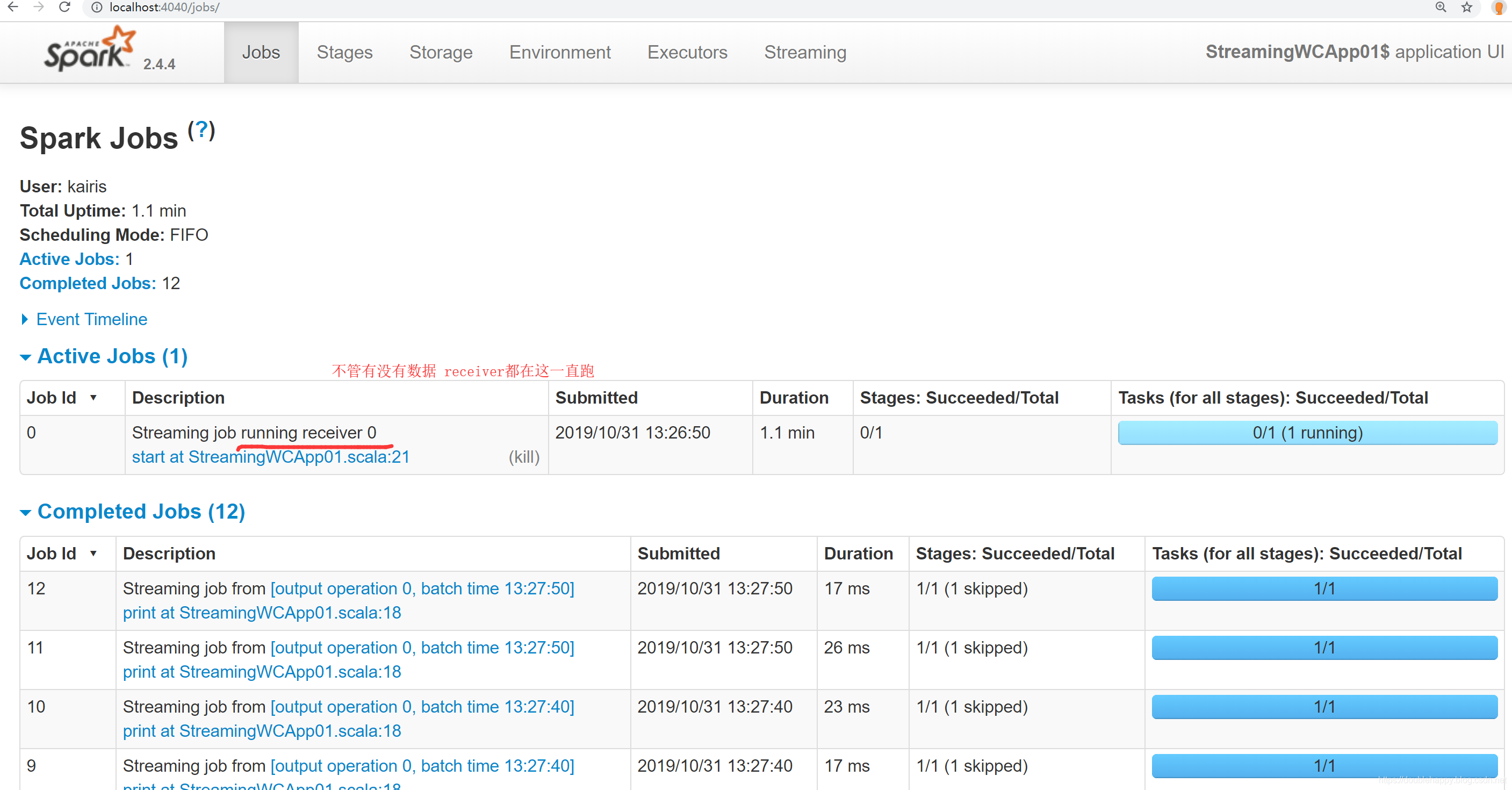
1 | active job : receiver 是接收数据用的 一直在跑 |
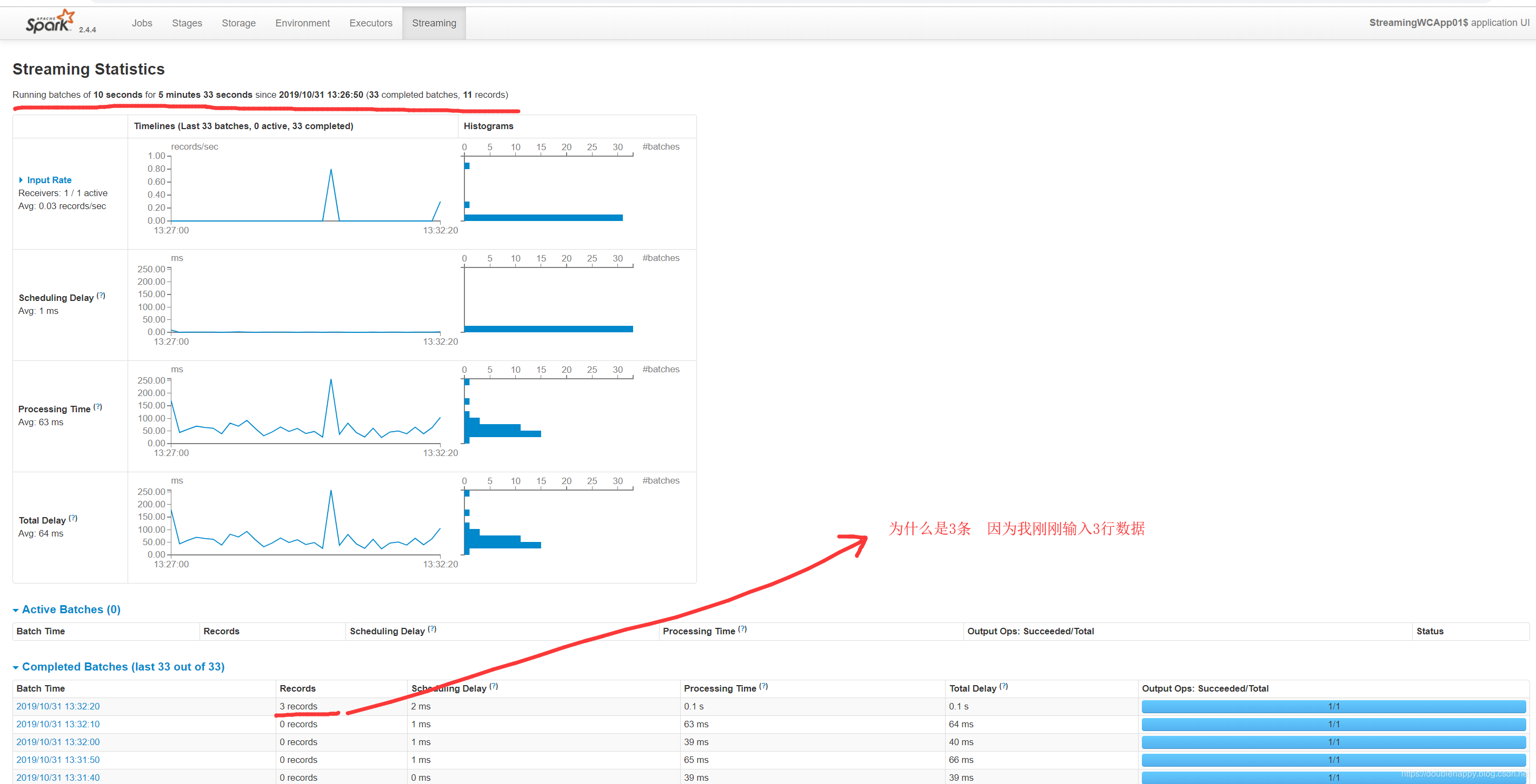
1 | 这幅图 调优的时候详细讲解 |
*操作讲解 *
Transformations on DStreams
只有最后两个和RDD算子不一样 其他的都一样
1 | [double_happy@hadoop101 ~]$ nc -lk 9999 |
1 | object StreamingWCApp01 { |
1 | [double_happy@hadoop101 ~]$ nc -lk 9999 |
1 | object StreamingWCApp01 { |
1 | /** |
1 | Spark Streaming provides two categories of built-in streaming sources. |
1 | 流处理系统 一般对接的是 kafka 读文件用的少 |