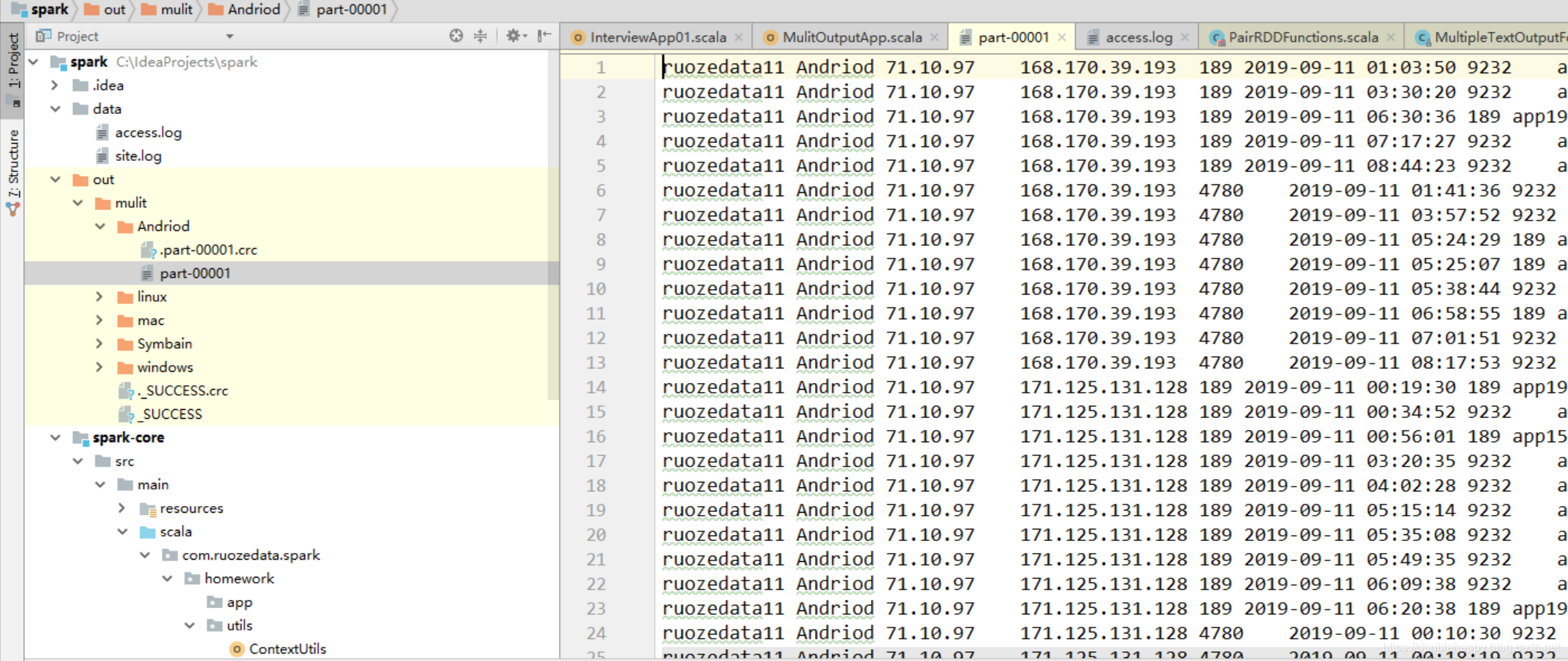
上次的结果输出的文本是这样的,客户说我需要压缩的格式呢?
生产上出来的数据非常非常大 肯定是需要压缩的
eg:5分钟数据量达到10多个G
1 | /** |
1 | object MulitOutputApp { |
学学底层的实现: 前面的文章好像有写 忘记了
1 | 1.saveAsHadoopFile |
补充知识点
1 | /** |
1 | object InterviewApp03ToMySQL { |
1 | object MySQLUtils { |
结果:
1 | mysql> select * from topn; |
1 | 能使用scalikejdbc 把数据写入MySQL更好哈 前面scala篇有讲 |
1 | 问题指出: |
1 | object InterviewApp03ToMySQL { |
结果:
1 | mysql> truncate table topn; //代码里加上删除之前的数据 可以解决 最好别truncate 只是学习时方便 |
Submitting Applications
工作当中是再idea里开发的 在生产上是在Submitting Applications
1 | 1.Spark-shell 底层调用的是Spark-submit |
1 | idea里面: |
1 | [double_happy@hadoop101 bin]$ ./spark-submit --help |
1 | spark-submit \ |
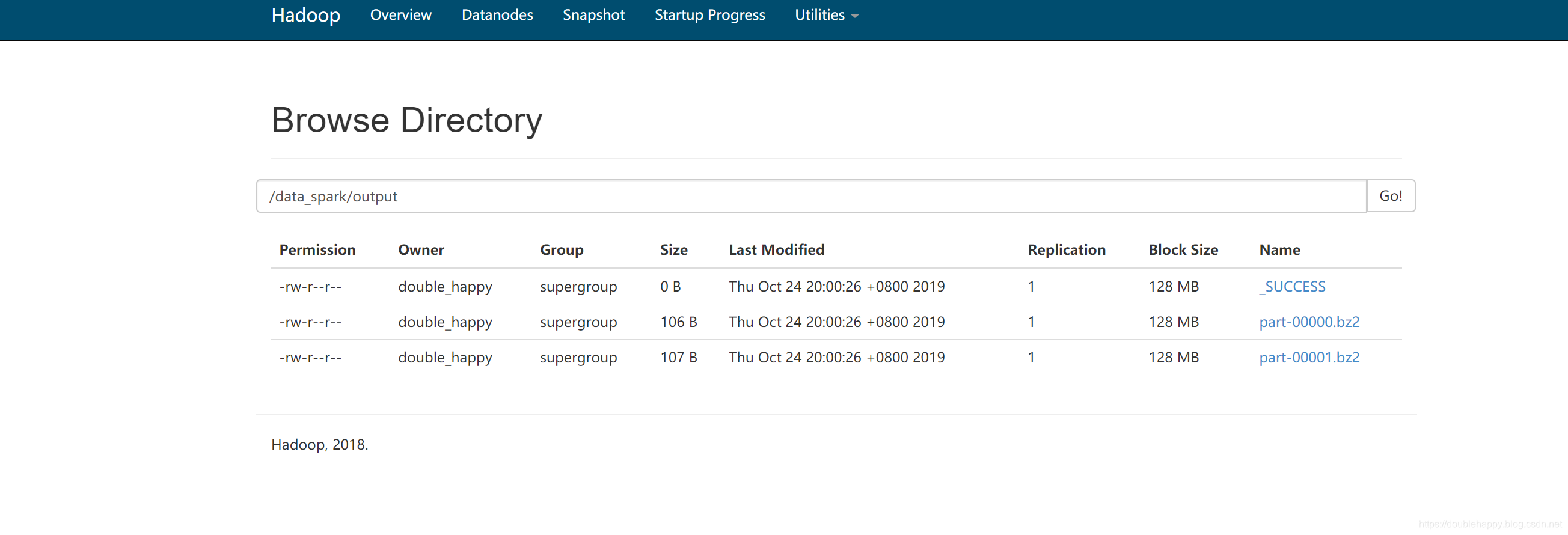
1 | [double_happy@hadoop101 lib]$ hadoop fs -text /data_spark/output/par* |
If your code depends on other projects, you will need to package them alongside your application in order to distribute the code to a Spark cluster. To do this, create an assembly jar (or “uber” jar) containing your code and its dependencies.
1 | 你的代码 依赖hadoop spark 但是这些集群本身 就有 打包的时候 要的是瘦包 如果需要第三方的包 |
1 | --jars JARS Comma-separated list of jars to include on the driver |
Loading Configuration from a File
The spark-submit script can load default Spark configuration values from a properties file and pass them on to your application. By default, it will read options from conf/spark-defaults.conf in the Spark directory.
1 | spark-submit 默认会加载 conf/spark-defaults.conf in the Spark directory |
以上是最基本的操作
它默认走的是 spark-defalut.xml 那么底层的实现一定是走的默认参数的
Monitoring
上面跑的程序
1 | 成功完之后 SC被干掉了 UI上面还能看到么? |
1 | scala> sc.parallelize(List("a","c","c","a","b","b","d")).map((_,1)).reduceByKey(_+_).collect |
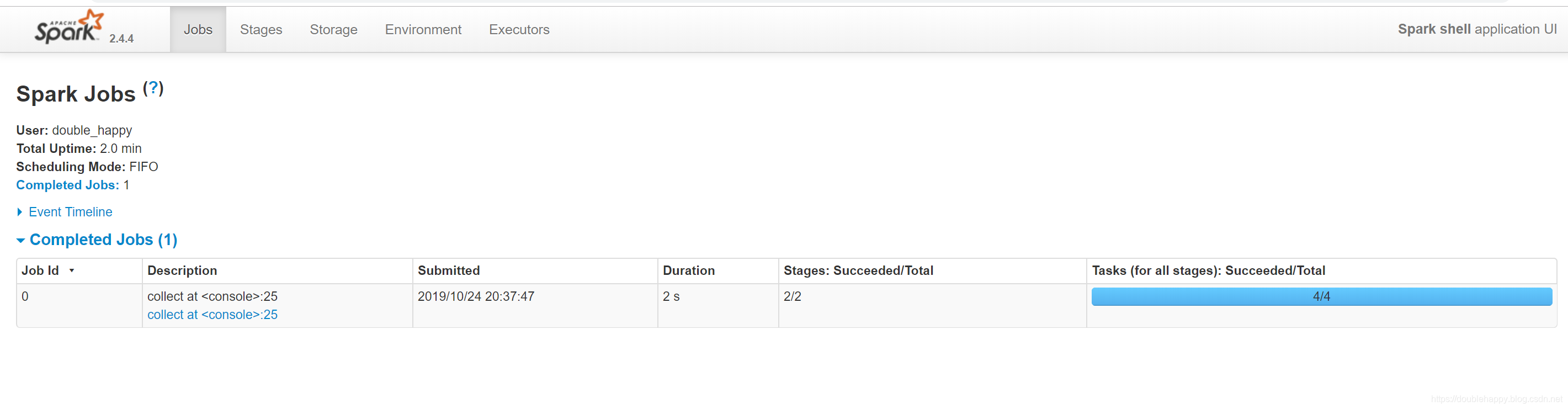
Every SparkContext launches a web UI, by default on port 4040, that displays useful information about the application. This includes:
A list of scheduler stages and tasks
A summary of RDD sizes and memory usage
Environmental information.
Information about the running executors
1 | 1.页面上展示 有多少个job (就是代码里有多少个action) |
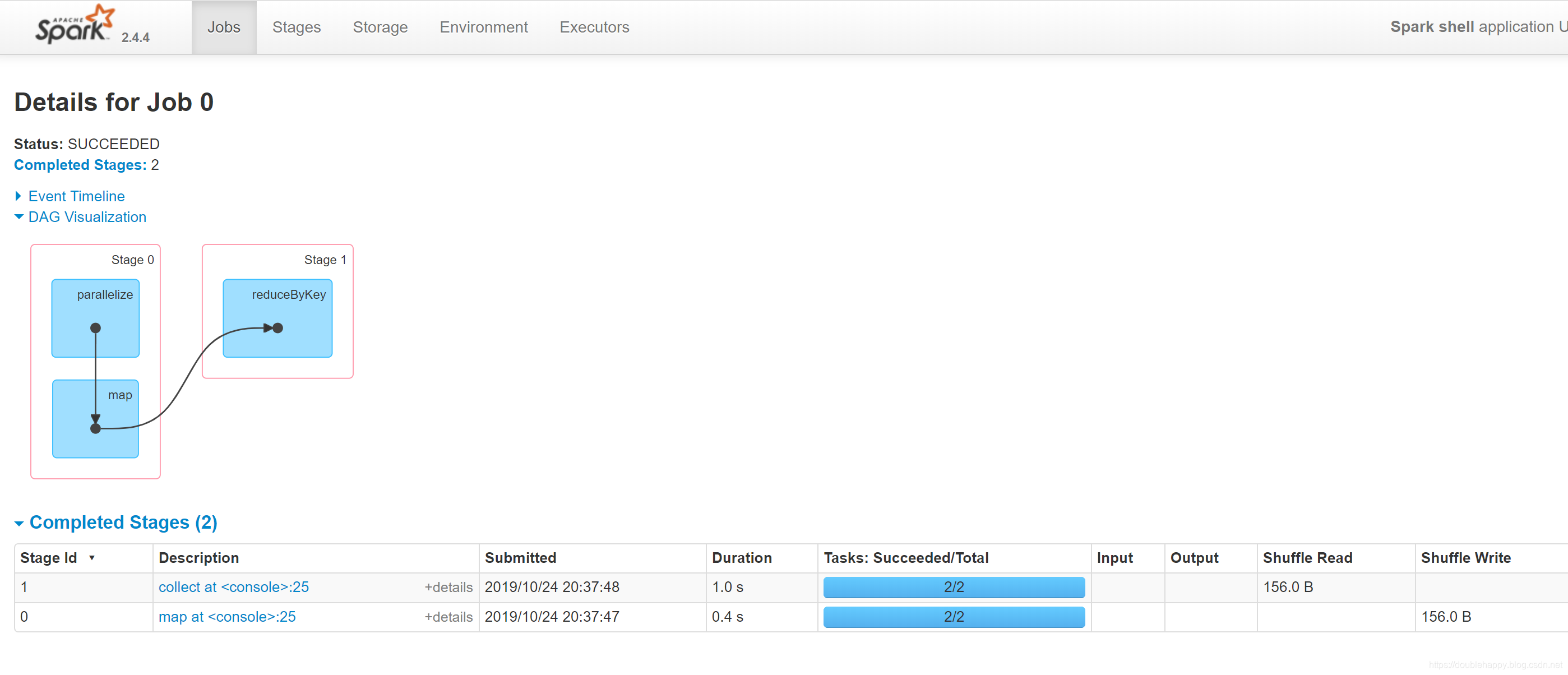
1 | 3.一个stage有几个task呢?点进去 |
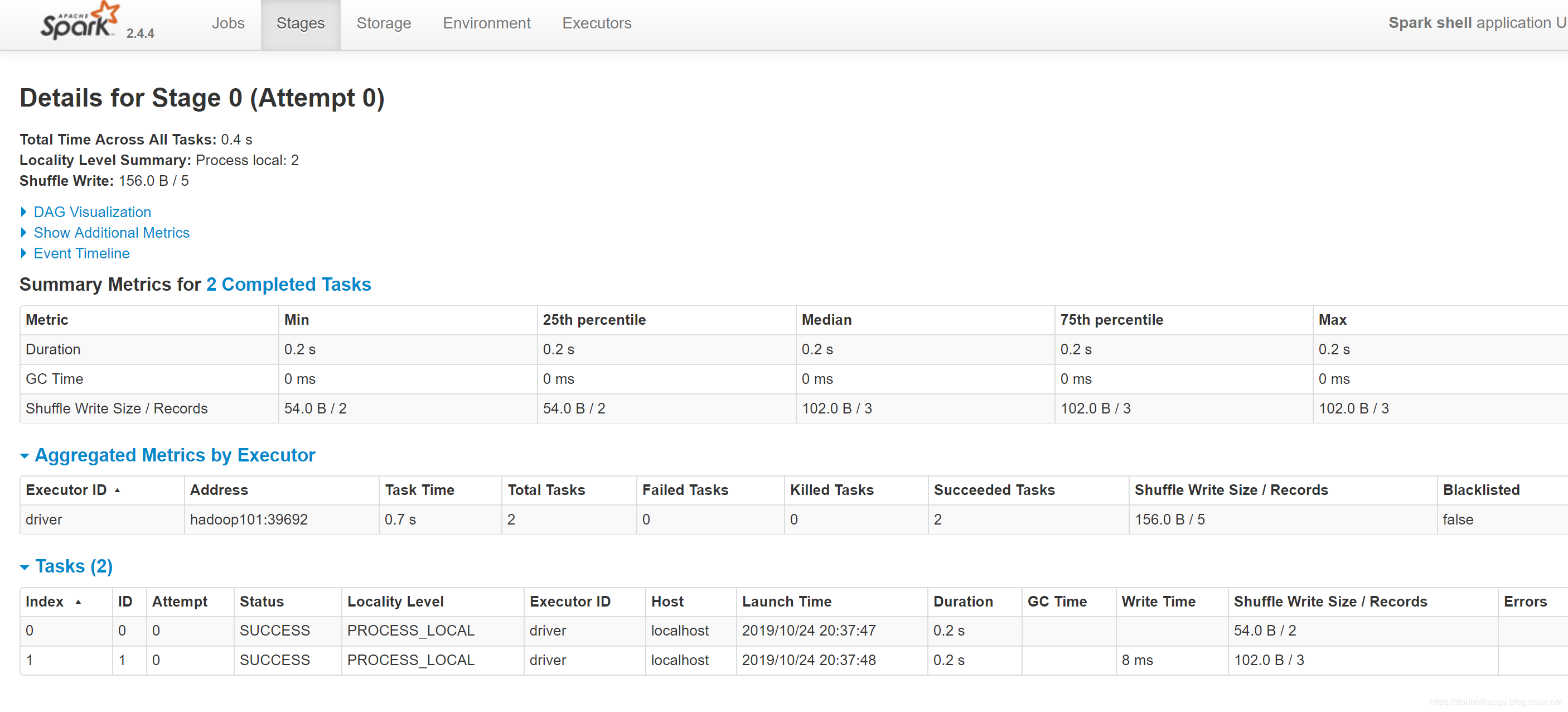
1 | Information about the running executors: |
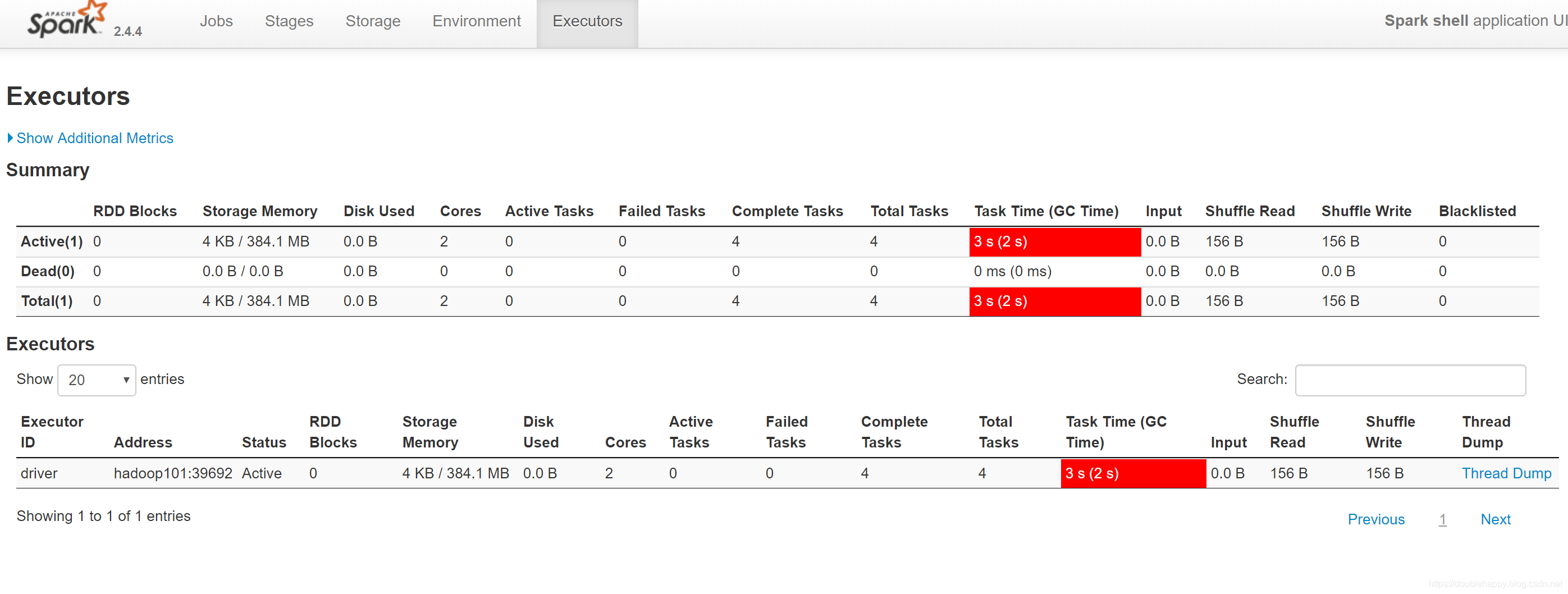
这副图运行时间慢的原因是 :
emmm 总有贪小便宜的人 去我云服务器上挖矿 悄踏玛真的很烦 因为我把端口全部开放了
If multiple SparkContexts are running on the same host, they will bind to successive ports beginning with 4040 (4041, 4042, etc).
这句话挺重要的 因为之前在公司里 我喜欢用 yarn client模式 而我提交的任务比较多
达到特别多的时候 再提交任务 是排不上的哈 提交不上的
Note that this information is only available for the duration of the application by default. To view the web UI after the fact, set spark.eventLog.enabled to true before starting the application. This configures Spark to log Spark events that encode the information displayed in the UI to persisted storage.
1 | Note that this information is only available for the duration of the application by default |
那么怎么构建 总结的UI呢?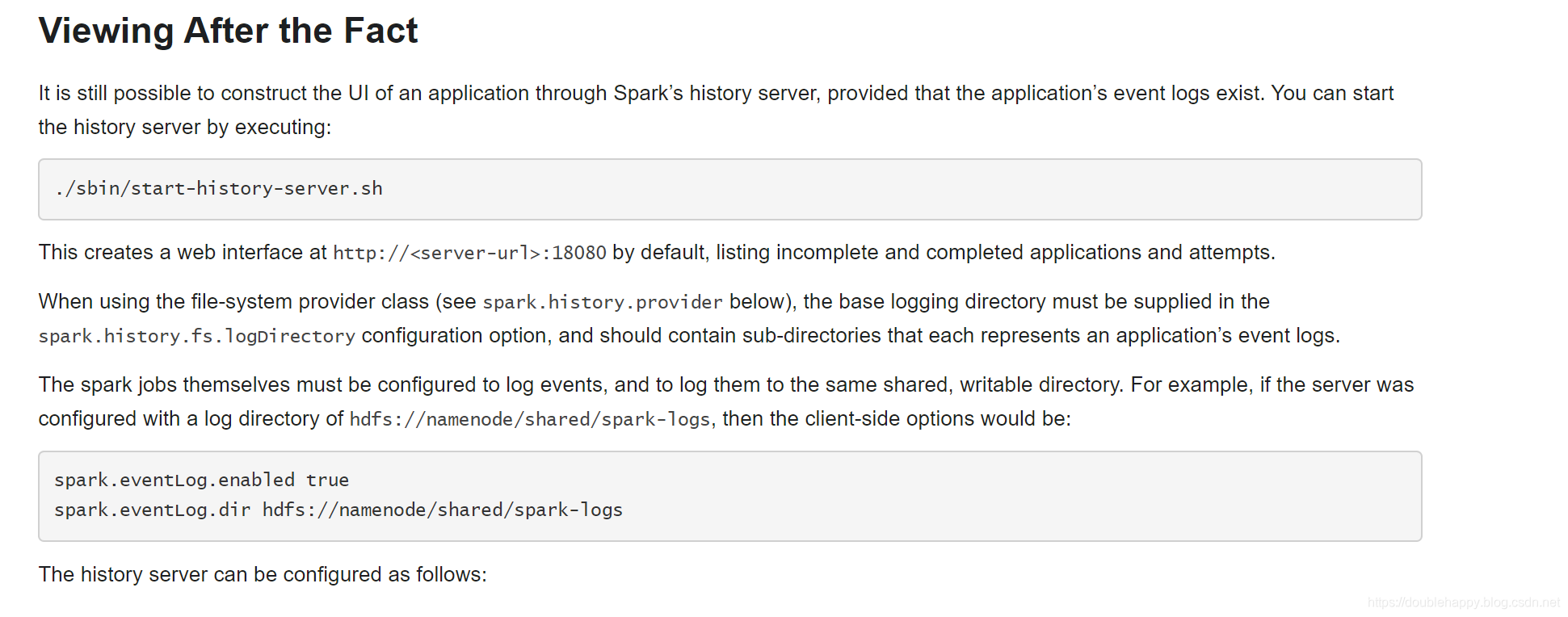
1 | 1.spark.eventLog.enabled true 开关打开 |
1 | [double_happy@hadoop101 conf]$ cat spark-defaults.conf |
This creates a web interface at http://
1 | 1.completed 和 incomplete spark怎么区别呢 需要一个刷新时间 |
配置一下 :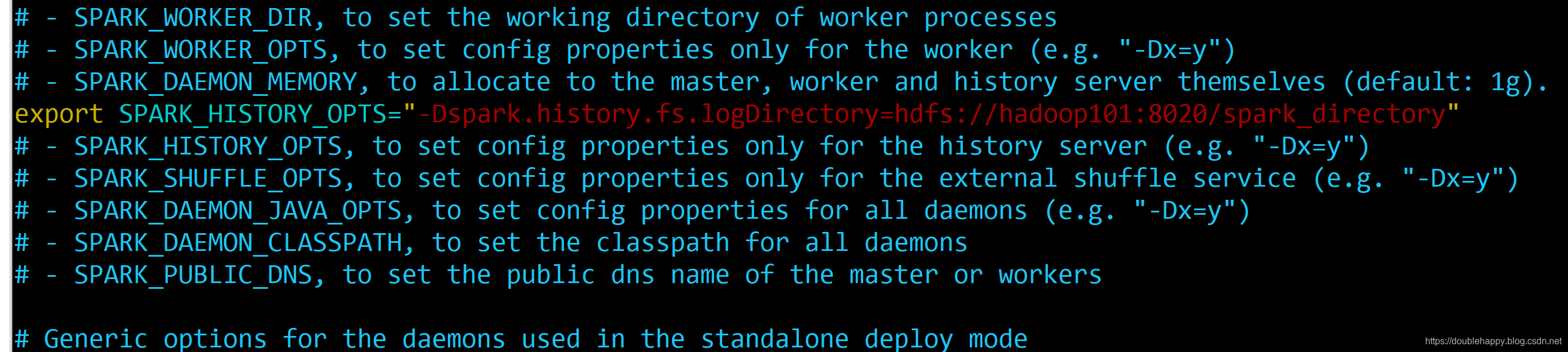
启动:
1 | 1.hdfs 上创建 log 文件夹 |
1 | [double_happy@hadoop101 sbin]$ ./start-history-server.sh |
说明启动ok
1 | 测试: |
1 | 1. |
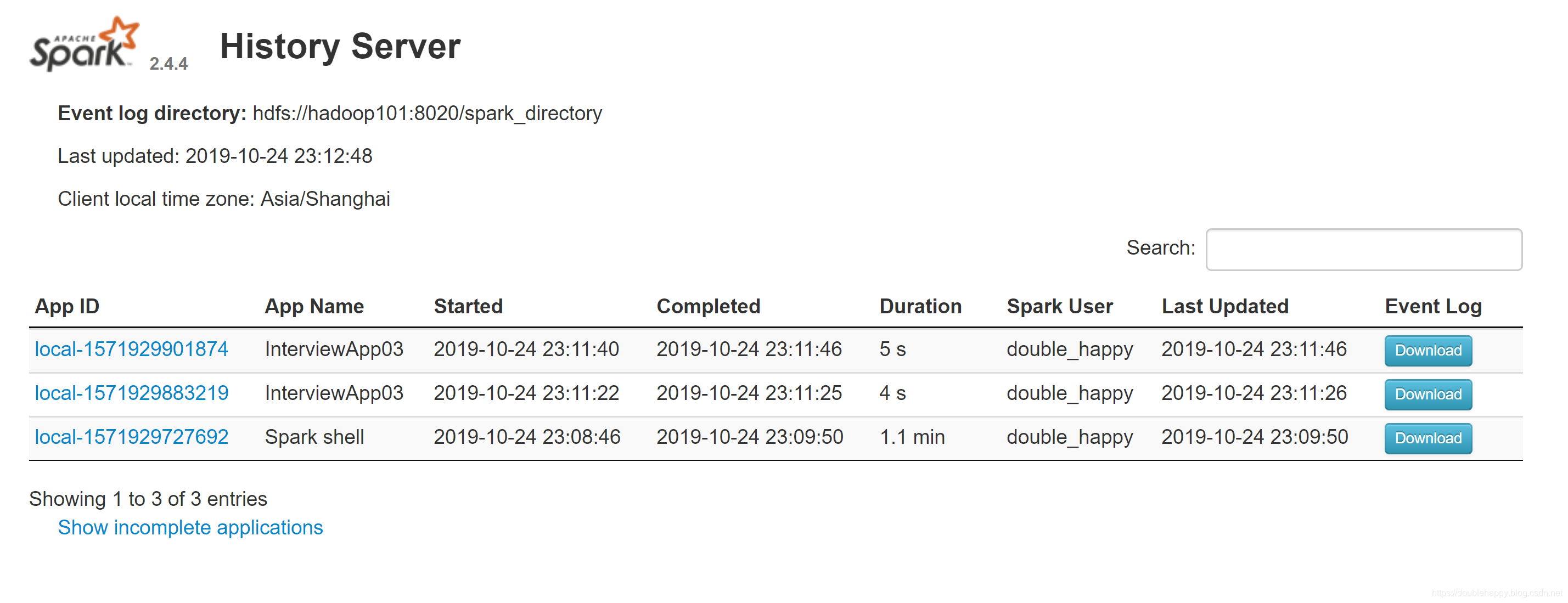
Note that in all of these UIs, the tables are sortable by clicking their headers, making it easy to identify slow tasks, data skew, etc.
Note
1.The history server displays both completed and incomplete Spark jobs. If an application makes multiple attempts after failures, the failed attempts will be displayed, as well as any ongoing incomplete attempt or the final successful attempt.
2.Incomplete applications are only updated intermittently. The time between updates is defined by the interval between checks for changed files (spark.history.fs.update.interval). On larger clusters, the update interval may be set to large values. The way to view a running application is actually to view its own web UI.
3.Applications which exited without registering themselves as completed will be listed as incomplete —even though they are no longer running. This can happen if an application crashes.
4.One way to signal the completion of a Spark job is to stop the Spark Context explicitly (sc.stop()), or in Python using the with SparkContext() as sc: construct to handle the Spark Context setup and tear down.
1 | 4.就是你代码里 sc.stop() 写了 程序完成后会显示在 completed 里面 如果不写会显示在incomplete |
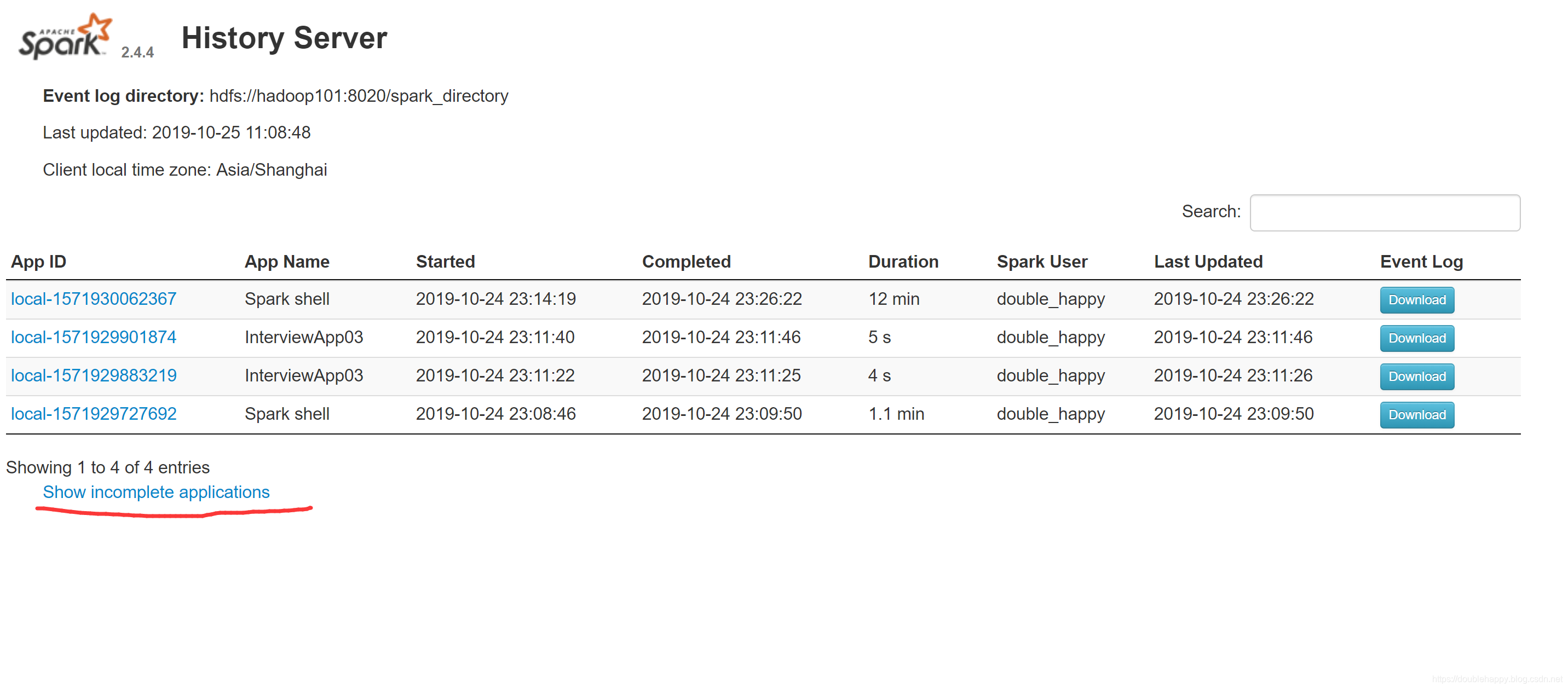
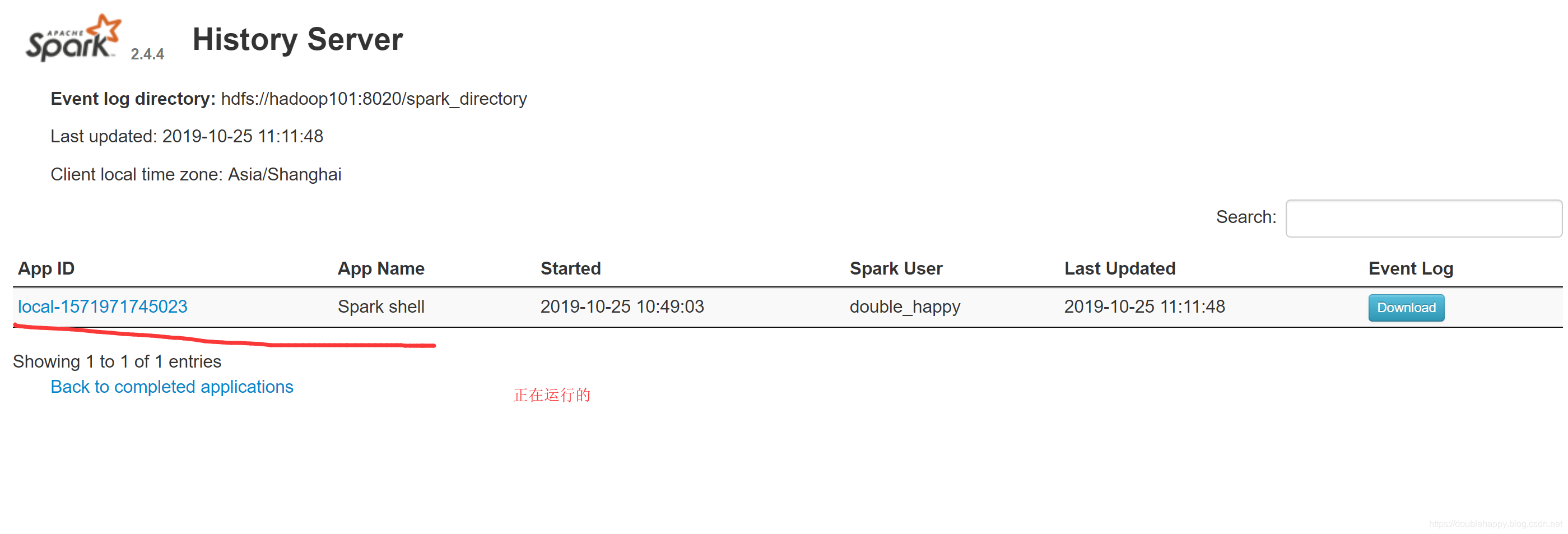
1 | 1.本地运行的作业 全部以 local开头的 |
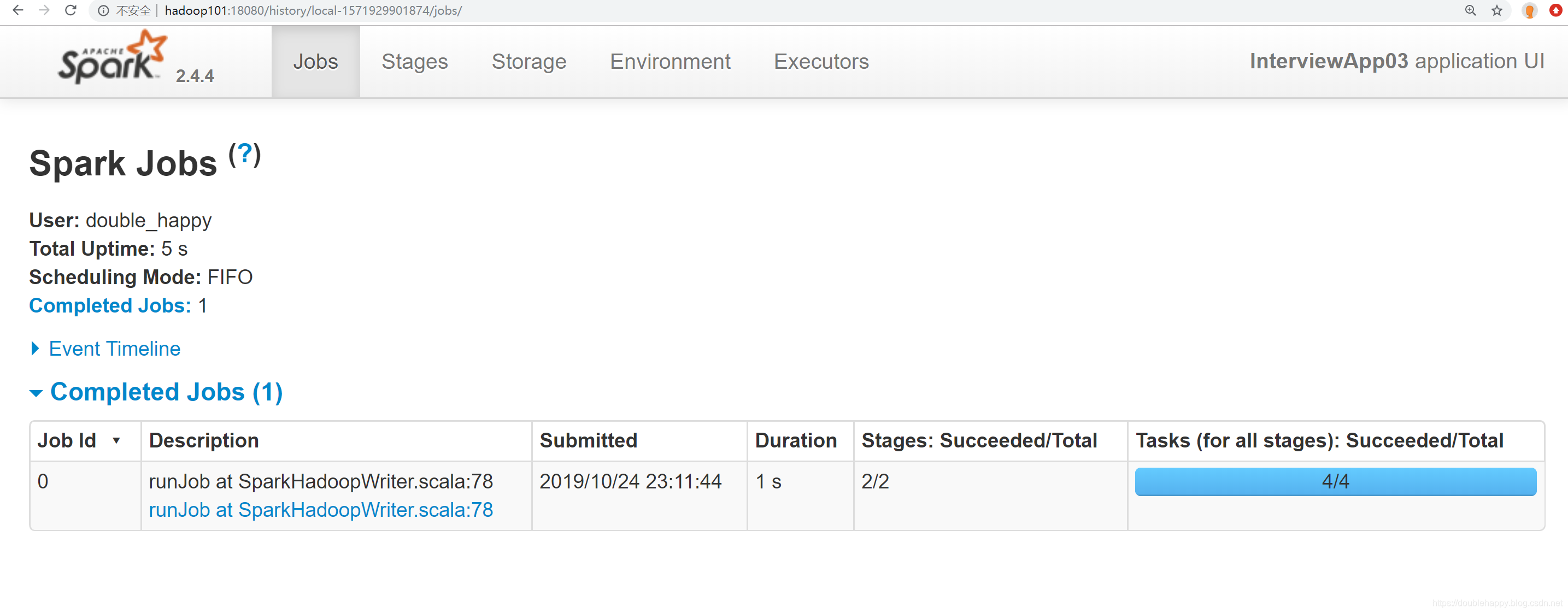
这个页面不就回来了么 程序已经运行完了 测试成功。
1 | Download 之后就是个Json文件 也可以去HDFS上去看我配置的log目录 也可以下载的 |
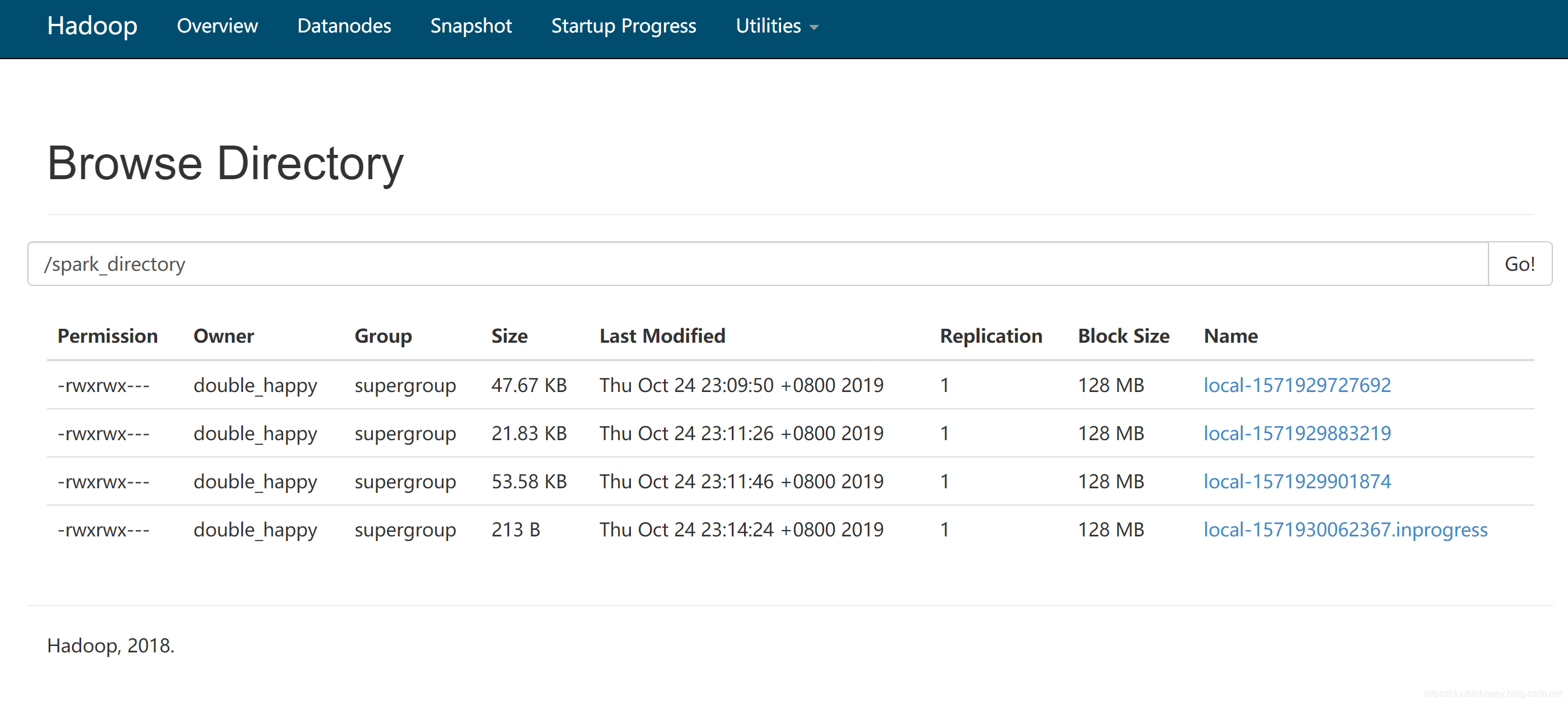
start-history-server.sh
1 | [double_happy@hadoop101 sbin]$ cat start-history-server.sh |
1 | 去idea里找到 HistoryServer类: |
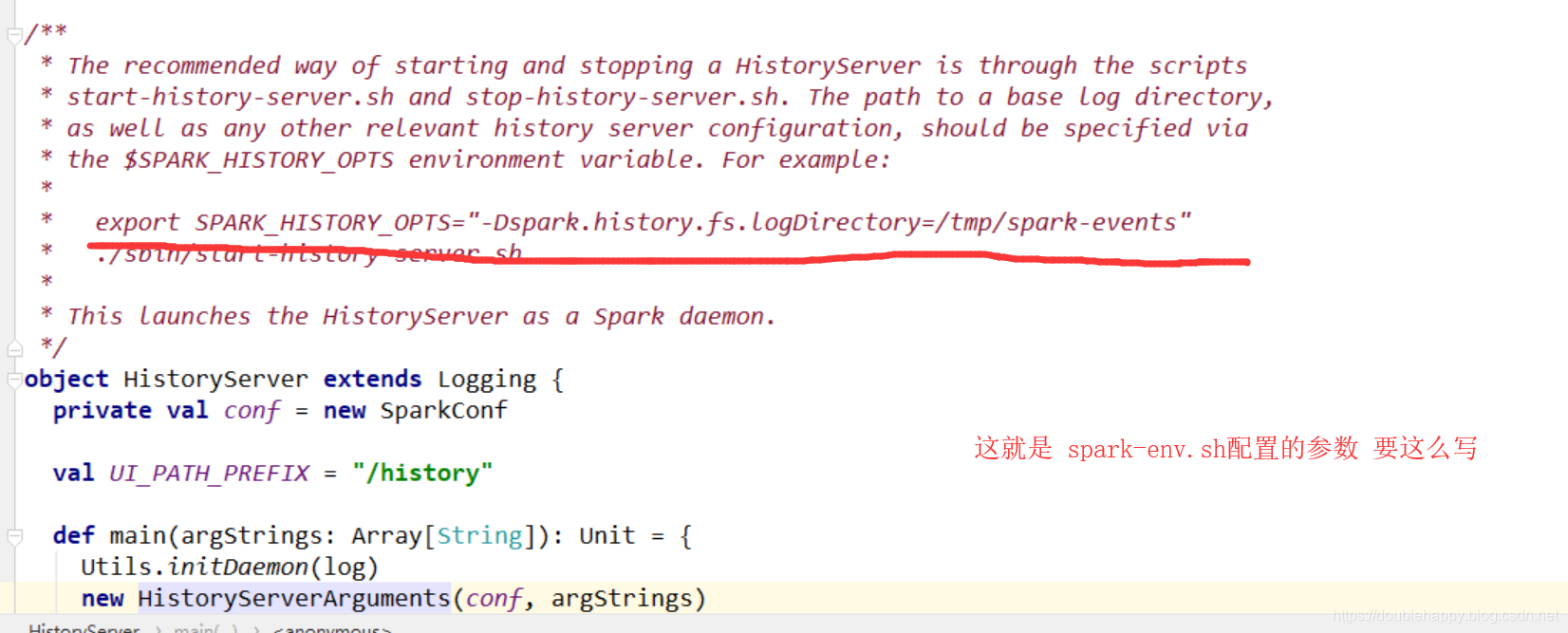
1 | 源码里有写: |
闭包

Shared Variables
Shared Variables
Normally, when a function passed to a Spark operation (such as map or reduce) is executed on a remote cluster node, it works on separate copies of all the variables used in the function. These variables are copied to each machine, and no updates to the variables on the remote machine are propagated back to the driver program. Supporting general, read-write shared variables across tasks would be inefficient. However, Spark does provide two limited types of shared variables for two common usage patterns: broadcast variables and accumulators.
Accumulators are variables that are only “added” to through an associative and commutative operation and can therefore be efficiently supported in parallel.
Spark natively supports accumulators of numeric types, and programmers can add support for new types.
1 | accumulators: |
1 | scala> val accum = sc.longAccumulator("My Accumulator") |
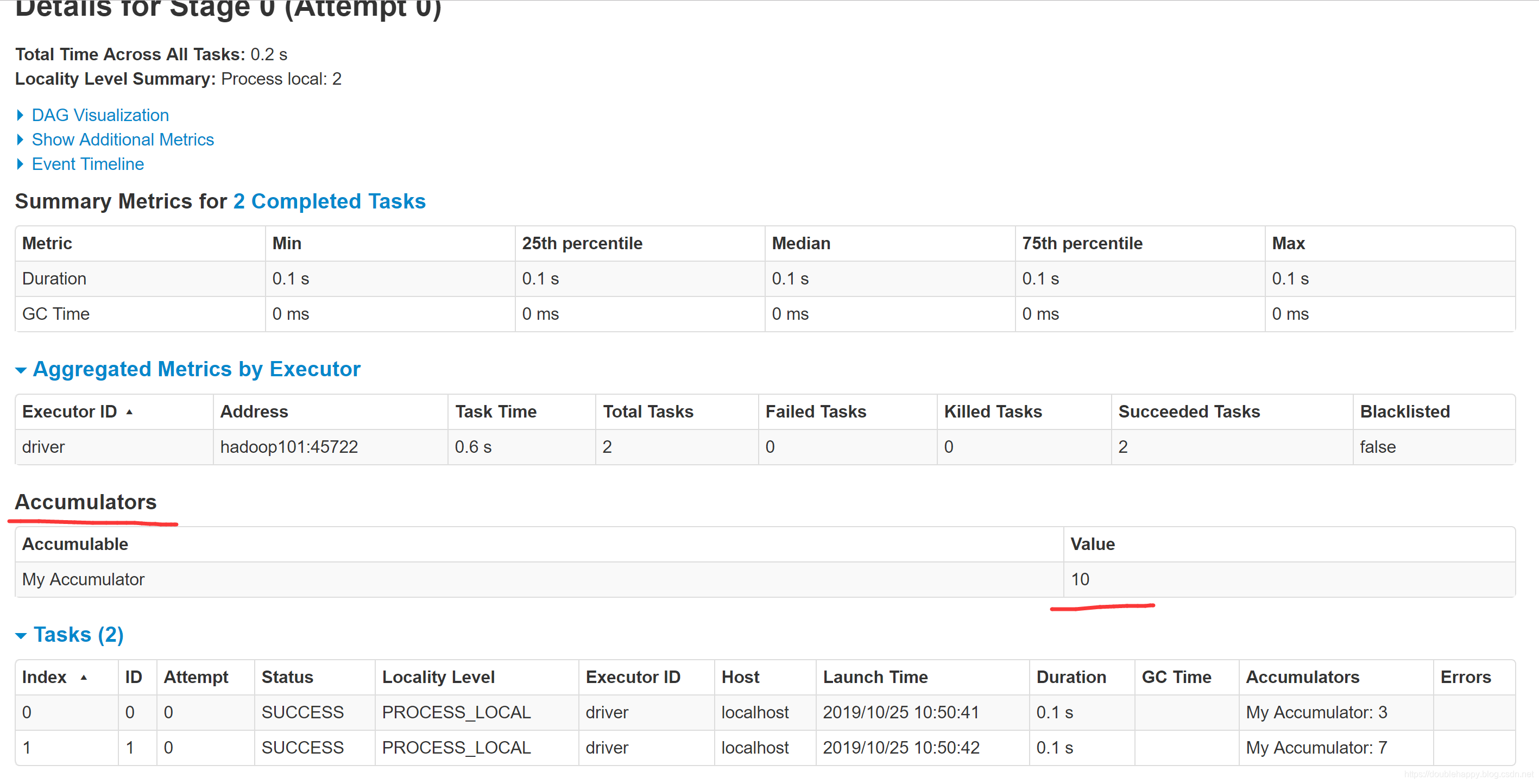
1 | 现在的计数器都是AccumulatorV2 版本 官网上写了如何自定义累加器 生产上我没用用过 |
案例:
1 | object InterviewApp03 { |
1 | broadcast variables : |
Broadcast variables allow the programmer to keep a read-only variable cached on each machine rather than shipping a copy of it with tasks.
1 | eg:这个代码 |
1 | object RDDOperationApp02 { |
1 | scala> val rdd1 = sc.parallelize(Array(("23","smart"),("9","愤怒的麻雀"))).collectAsMap() |
sparkcore之后sparksql 以及sparkstreaming 、sss、spark调优 的重要的文章是进行私密的 我写博客的目的是为了做笔记 为了学习