核心术语Glossary
1 | 核心术语 |
Application
User program built on Spark. Consists of a driver program and executors on the cluster.
1 | 1.User program built on Spark |
Application jar
A jar containing the user’s Spark application. In some cases users will want to create an “uber jar” containing their application along with its dependencies. The user’s jar should never include Hadoop or Spark libraries, however, these will be added at runtime.
Driver program
The process running the main() function of the application and creating the SparkContext
1 | 1. running the main() function of the application |
Cluster manager
An external service for acquiring resources on the cluster (e.g. standalone manager, Mesos, YARN)
所以你的代码里 上传到集群的时候 不要写 死 appname 和 master
到时候通过 spark-submit 来指定就 可以选择 外部的cluster
Deploy mode
Distinguishes where the driver process runs. In “cluster” mode, the framework launches the driver inside of the cluster. In “client” mode, the submitter launches the driver outside of the cluster.
一切以yarn为主
1 | YARN: RM NM(container) |
Worker node
Any node that can run application code in the cluster
1 | yarn模式下 就是 nm |
Executor
a process launched for an application on a worker node, that runs tasks and keeps data in memory or disk storage across them. Each application has its own executors.
一个进程 jps 就能看到
对应yarn上 就跑在 nm的container里的
1 | 1. runs tasks |
Task
A unit of work that will be sent to one executor
1 | 1.task 是发送到 executor里的 |
Job
A parallel computation consisting of multiple tasks that gets spawned in response to a Spark action (e.g. save, collect); you’ll see this term used in the driver’s logs.
1 | 1.一个action算子对应一个job |
Stage
Each job gets divided into smaller sets of tasks called stages that depend on each other (similar to the map and reduce stages in MapReduce); you’ll see this term used in the driver’s logs.
1 | 1.一组task的集合 叫一个stage |
总结案例
1 | eg: |
Components ***
Spark applications run as independent sets of processes on a cluster
independent sets of processes:就是executor
Spark applications run as independent sets of processes on a cluster, coordinated by the SparkContext object in your main program (called the driver program).
Specifically, to run on a cluster, the SparkContext can connect to several types of cluster managers (either Spark’s own standalone cluster manager, Mesos or YARN), which allocate resources across applications. Once connected, Spark acquires executors on nodes in the cluster, which are processes that run computations and store data for your application. Next, it sends your application code (defined by JAR or Python files passed to SparkContext) to the executors. Finally, SparkContext sends tasks to the executors to run.
1 | 1. which allocate resources across applications. which ===》 cluster managers |
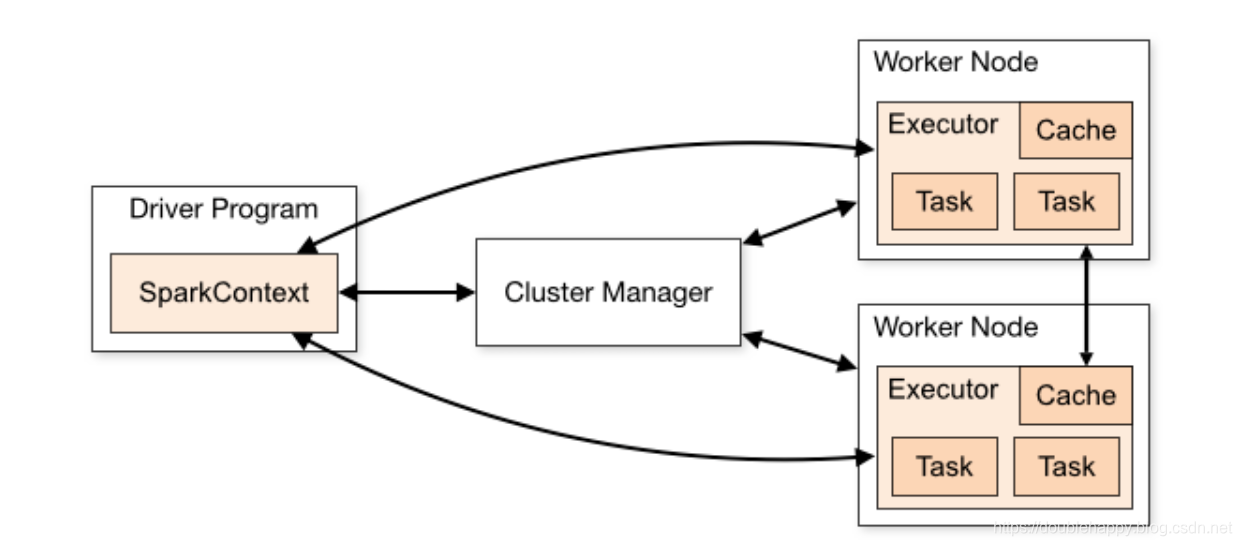
1 | 1.driver : main方法里有个 sc |
There are several useful things to note about this architecture:
1.Each application gets its own executor processes, which stay up for the duration of the whole application and run tasks in multiple threads. This has the benefit of isolating applications from each other, on both the scheduling side (each driver schedules its own tasks) and executor side (tasks from different applications run in different JVMs). However, it also means that data cannot be shared across different Spark applications (instances of SparkContext) without writing it to an external storage system.
2.Spark is agnostic to the underlying cluster manager. As long as it can acquire executor processes, and these communicate with each other, it is relatively easy to run it even on a cluster manager that also supports other applications (e.g. Mesos/YARN).
1 | 1. which stay up for the duration of the whole application and run tasks in multiple threads |
3.The driver program must listen for and accept incoming connections from its executors throughout its lifetime (e.g., see spark.driver.port in the network config section). As such, the driver program must be network addressable from the worker nodes.
4.Because the driver schedules tasks on the cluster, it should be run close to the worker nodes, preferably on the same local area network. If you’d like to send requests to the cluster remotely, it’s better to open an RPC to the driver and have it submit operations from nearby than to run a driver far away from the worker nodes.
1 | 1.The driver program must listen for and accept incoming connections from its executors throughout its lifetime |
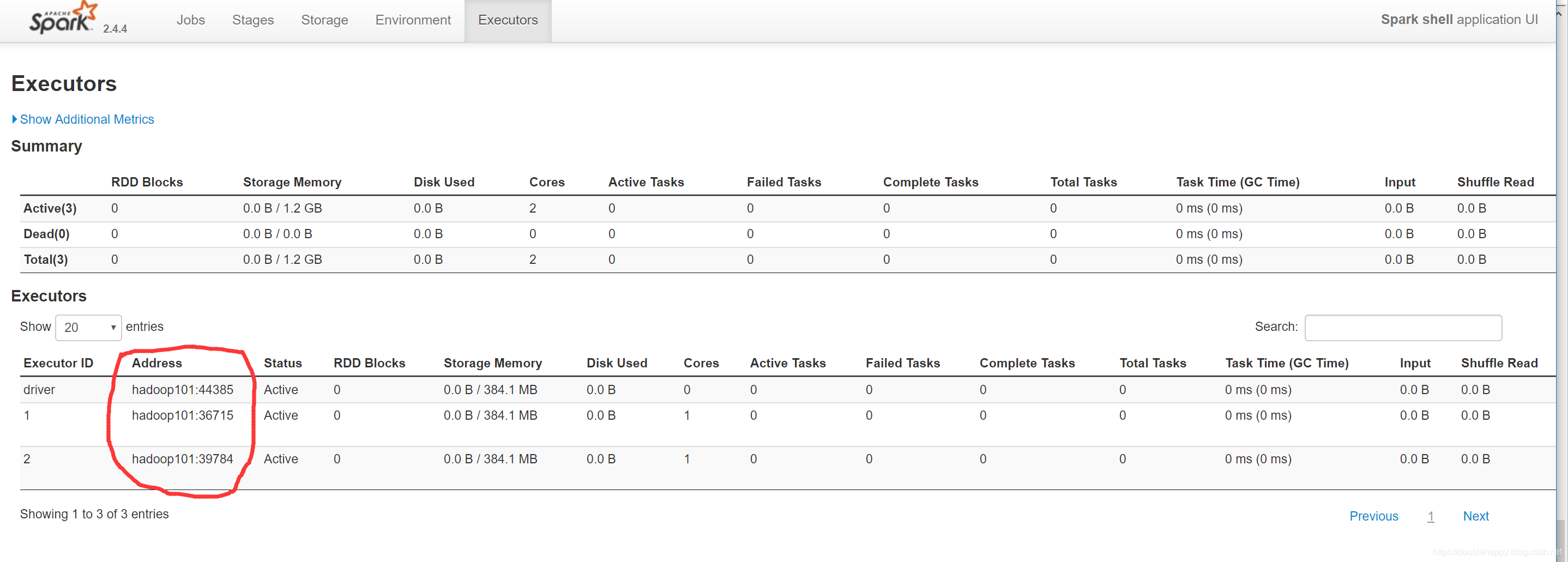
这块可以看到 executor 在那台机器的哪个端口上
1 | 2.As such, the driver program must be network addressable from the worker nodes. |